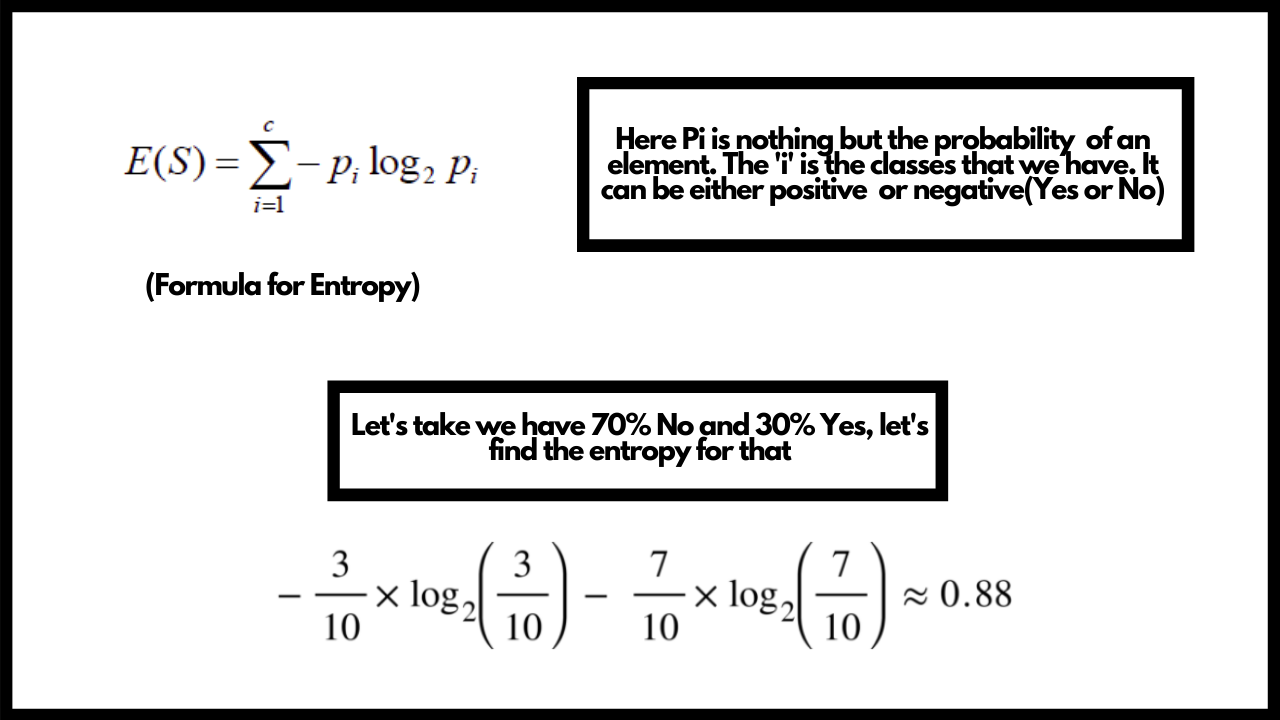
Decision Tree
When we talk about classification type problem statement, one of the most common algorithm that people tend to go with is Decision tree. Let's try to understand Decision tree and how does it work exactly. This algorithm can be used for both classification and regression but in most cases it is used for classification. In decision tree we split our data into different nodes in the tree. For the splitting purpose we use something known as Entropy that helps us in selecting the right features to split our data inorder to make our decision tree. Entropy helps us to determine the purity of a split. A pure subsplit means we either get a value of 0 or 1(Yes or No). The goal in Decision tree is to get to the leaf node as quickly as possible. For this purpose we need to select the right features and parameters. Whenever we perform a split, we need to calculate the purity of the split and this is where we use Entropy. Let's say we need to classify whether a car will be sold or not given it's different properties and features. Let's see how we can calculate the entropy and determine the split for the above case.
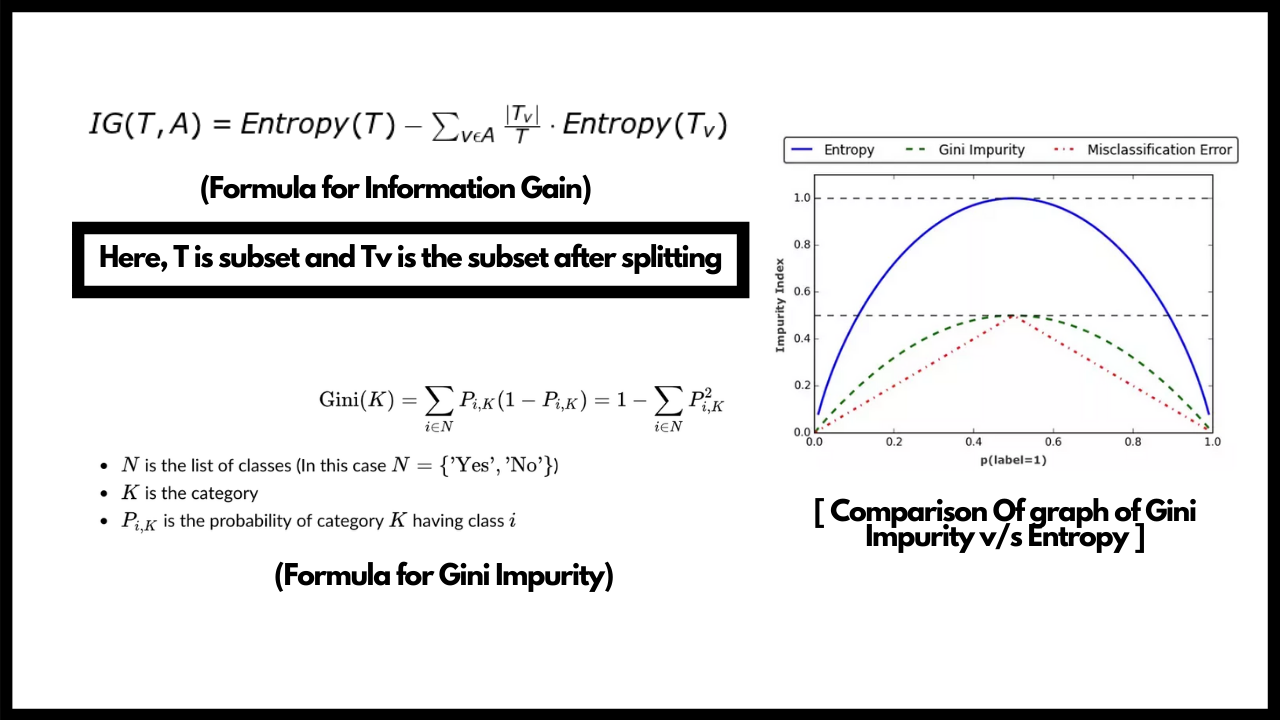
We also need to understand a term known as Information gain. We use information gain to device our root node for the tree. We take the average of all the entropies based on a specific split. On paper this is a long process but for our system it is a very small task. We need to select that split which has the highest information gain for making our decision tree. Once we have our root node, we can either calculate the entropy for rest of the splits and use those splits which have the least entropy or go with a faster approach and use Gini Impurity. Gini impurity is used over entropy in ensemble as it is faster and takes computationally less time as it doesn't contain any logarithmic calculation in it's formula which usually takes more time to compute.
Decision trees have one disadvantage. They suffer from the problem of overfitting as the decision trees tend to perform very well on training data but fail to perform on testing data. This is what we call having low bias and high variance. This problem can be overcome with help of decision tree pruning or just using Random forests. We will learn about them next as they are based on Decision trees. Now we know how decision trees work so let's quickly summarize everything we just learnt.
- Decision trees can be used for both classification and regression problem statement but it is mostly used for classification.
- We make use of Information gain to get the Root node and then use either Entropy or Gini impurity to determine the further splits and to determine what features to use for the split. We choose the value which is lower when we compare entropies of 2 nodes and these values will be between 0 and 1.
- We keep splitting untill we reach the leaf node, the goal is to reach this leaf node as quickly as possible.
- Decision trees have low bias and high variance which is the condition for overfitting. We can eliminate this by using Decision tree pruning or using Random forest about which we will study in the next section.
With this we come to an end to the Decision Trees theory and we can go on to the Notebooks and Hands-On exercises.
Implementation Walkthrough
Learn this section on Google Colab.