Random Forest
Now that we know about Decision trees, let's look at another algorithm that uses these decision trees in order to give much better results. Random forest is an Ensemble technique which simply means that it is not a single model but a combination of multiple models. In ensembling, we have 2 main techniques: Bagging and Boosting. In Random forest, we use Bagging whereas in algorithms like Adaboost, XGBoost make use of Boosting.
Let's take a real life example here. Consider you have a data set with features of people and you need to classify whether the person is male or female. Random forest is mostly used for classification purpose but you can use it for regression tasks as well. The very first step in bagging is splitting the main data set into smaller sets to feed to different models. So we split our data set of features and feed it to differnt models, which in our case are the Decision trees. These features can be anything such as the length of hair, facial features, etc. After giving few records to our first model, we perform resampling before giving records to the next model. This step is called Row sampling with replacement.This steps is also known as Bootstrapping. Each models trains on their sample of data i.e the features of the person and when we give it the test data, the model makes a prediction or gives an output.
Once we have our outputs from the different models, we make use of a voting classifier. This helps us in considering the maximum outputs of one category. Basically, helps us in determing the output that has occured most number of times. This step is also known as Aggregation. Because of these steps, Bagging is also known as Bootstrap Aggregation.
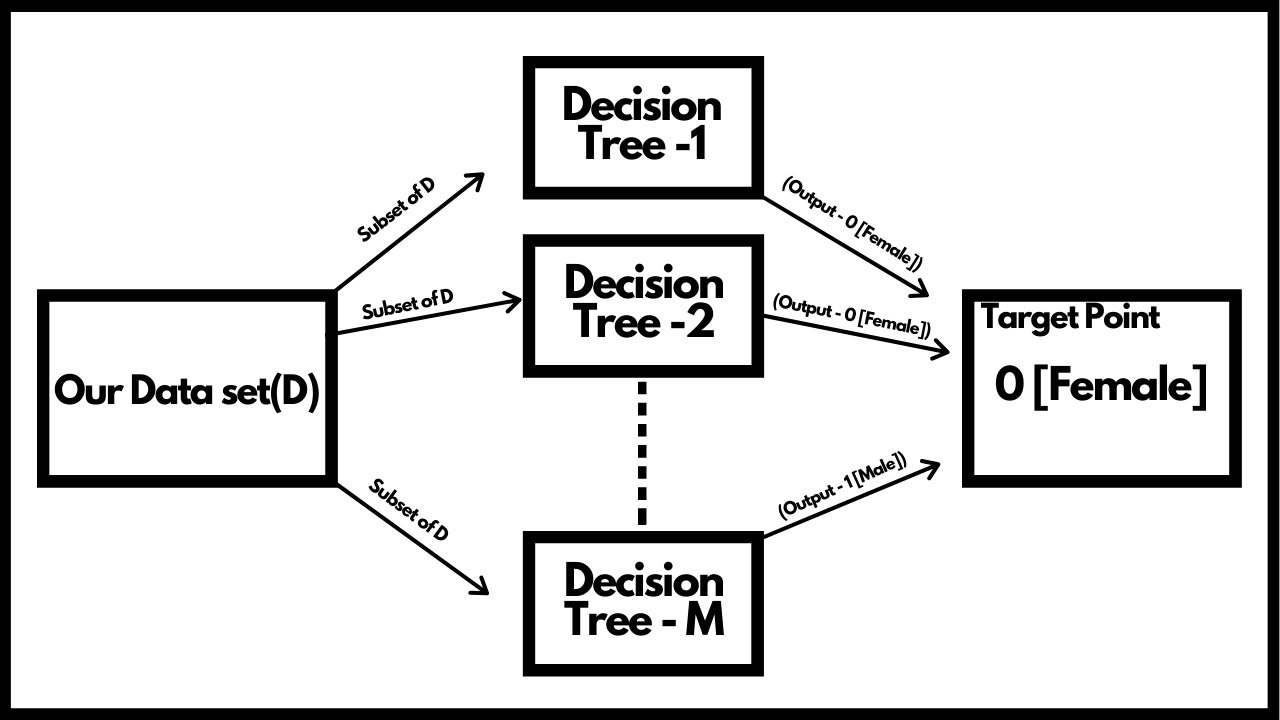
Now the question arises, why should we prefer using Random forest over Decison trees? To answer this we need to know about a very important property of decision trees. All decision trees have Low bias and high variance. This basically means that the model would perform very well on the training data but when it comes to testing data, it doesn't perform very well. We want our models to have low bias and low variance and hence using Random forest over a single decision tree helps a lot as it is a combination of multiple decision trees and we take the majority of the results given by these decision trees which automatically turns the high variance into low variance. Even if we change the samples in our data, suppose we change 500 entries out of 2000 entries in our features data set, it won't affcet the model as the records are anyway distributed in different manner after feature and row sampling. Hence, Random forest is preffered over Decision trees.
For regression tasks, the first step of bootstrapping will remain the same. After feature and row sampling and training our decision trees, when we feed in our testing data set we will get continuous values as outputs as it is a regression type problem statement. In our classifier we used the majority votes classifier but as we have continuous values, we take the mean of all the outputs given by our decision trees in order to get our final result. Even in Sklearn, the random forest algorithm takes the average of all the outputs given by the models.
This is how Random forest works. We will quickly sum everything up for you before you move onto your notebooks and hands-on activity.
- The algorithm starts by splitting the data that we have into smaller sub sets or records.
- These records are first fed to a model and then we carry out resampling before feeding the records to the next model. This step is referred to as Bootstrapping.
- The model trains on the data that it is fed and then when we pass the test data, each model gives an output.
- We then apply a voting classifier on these outputs and then we get our final output. This step is known as Aggregation.
This sums up our Random Forest algorithm. Please go through the notebooks and quiz.
Implementation Walkthrough
Learn this section on Google Colab.