Linear Regression
There are mainly three types of algorithms in Machine Learning, namely: Supervised, Unsupervised and Reinforcement Learning. Since, Linear Regression is a Supervised Machine Learning algorithm , we'll focus on that for this topic.
Supervised Machine Learning means that the algorithm is first trained on a labelled dataset (generally referred to as training data) to form a model. After this, the machine is provided with a new set of data (known as the test data), and the model uses the acquired knowledge to predict the outcomes for this test data. For instance, when we were kids, our parents taught us what a cow, rabbit, snake, squirrel, etc. are. In other words, they trained us. After that, whenever we see an animal now (test data), we are able to classify it depending on our knowledge. This is Supervised Learning.
Supervised ML algorithms are of 2 types:
- Classification: In this, the output variable is a category (discrete, categorical target variable)
- Regression: In this, the output variable is a value (continuous target variable)
Let's talk about regression now.
The term "regression" means "coming back to the average".
Regression Analysis is a mathematical measure to determine the average relationship between two or more variables in terms of original units of data. In regression analysis, we have two types of variables: Dependent variable (target/output variable) and independent variable (predictor/input variable). The variable whose value is to be predicted is called dependent variable, whereas the variable which is used for prediction is called independent variable.
Simple linear regression is defined as Y = aX + b, where , Y is the dependent variable and X is the independent variable. a and b are coefficients, which we'll understand below by a simple example.
Let us assume that marks scored by a student in exams is only related to number of hours he studied. We went to a class and collected data on marks scored and study-hours of various students. This data is represented by blue dots in the figure below.
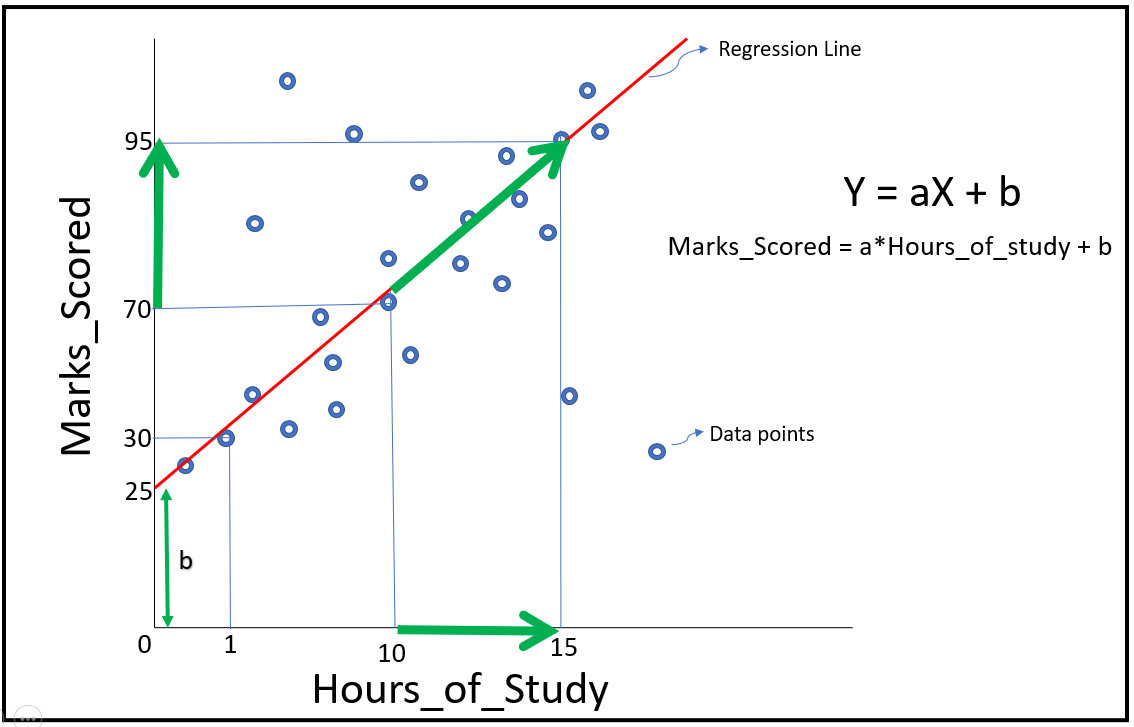
The straight line (red color) is called best fit line or regression line. It is called best fit because the error between the predicted values and the observed values is minimum for this line. Now as we can see, a student can score 25 marks even if they don't study at all. This is called intercept or the value of "b". You can also see that with increase in hours of study, marks increase (as shown by the green arrows). The value of "a" in the equation represents change in units of Y per unit of X. Thus , "a" is the slope of the best fit line. As we know, slope of line is (y2-y1)/(x2-x1). Thus, a = (95-70)/(15-10) = 5 . Thus , equation becomes Y = 5X + 25 . So, now with any value of X, we can find a value of Y. For example, when X=1, Y would be 30. This is how we are able to establish a mathematical relationship between 2 variables, which can be used for predictive purposes.
The above explanation was for a simple linear regression. But in real life, we generally have a large number of independent variables which are used to predict value of the dependent variable.
Mathematically,

Now, that we have learned the mathematical/statistics part behind linear regression, let's move forward and learn how this is used in Machine Learning. First, we'll go through linear regression algorithm from scratch to learn how linear regression works behind the scene. Once you've completed that, move on to the second link provided below to see how you can perform linear regression using the Scikit-Learn library.
Want to know how to implement linear regression algorithm from Scratch? Follow this link: https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1-q7YKL852EHdiNheQSXATmfBynjqT_7Y?usp=sharing
Check this link to see how to use linear regression algorithm using Sklearn Library: https://github.com/Anjali001/GRIP_Tasks/blob/master/Linear_Regression.ipynb
References:
#
- Basic Econometrics by Damodar N. Gujrati
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/linear-regression-python-implementation/
- https://machinelearningmastery.com/linear-regression-for-machine-learning/
- https://medium.com/analytics-vidhya/linear-regression-using-scikit-learn-in-python-5703be8e4f38
Implementation Walkthrough
Learn Linear Regression on Google Colab.
Implementation Walkthrough
Learn Polynomial Regression on Google Colab.