K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN)
We have seen many Classification algorithms so far and now it is time for us to explore KNN. K-Nearest neighnors or KNN is a supervised learning technique which can be used for both classification and regression type problems. But mostly, KNNs are used for classification. Compared to others, KNN is very simple to understand and implement. Let's try to understand it with help of some examples and diagrams.
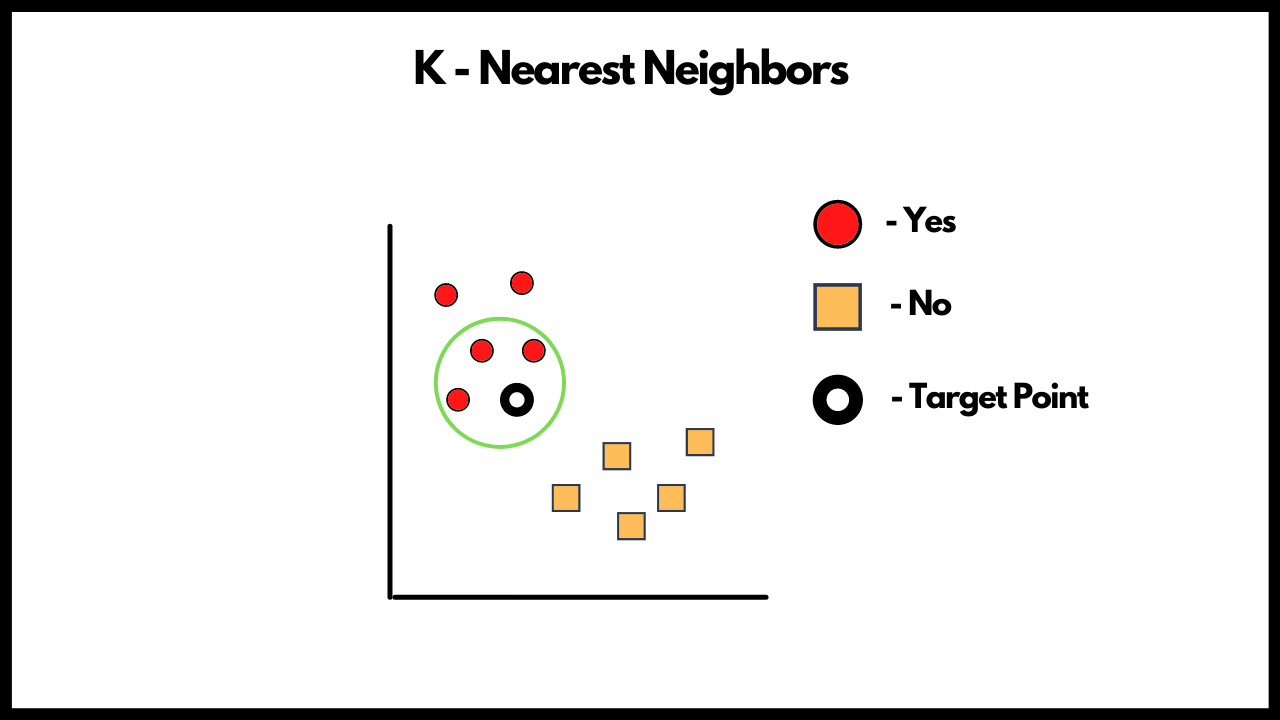
In the above diagram we have 2 classes, Yes and No. Let's assume that you want to get into a college and we have the data of your TOEFL scores, your GRE scores and College CGPA. We have a black point which is our target point. In KNN, we calculate the distance between our target point and the 'k' points that are close to it. So in the above case, we take the value of K as 3, when we apply KNN, we calculate the Euclidean distance between our target point and all the other points in the plane and the 3 points that are closest to our target points will determine our output. Maybe you have great TOEFL, GRE scores along with a good CGPA and hence in the abve case the 3 closest points to the target point fall in the class 'Yes'. Hence the model will give the output 'Yes'. You can also end up with the case where you have 2 points of 'Yes' class and 1 point of 'No' class but in all the cases the majority votes will win, this is an important point to remember. KNN is said to be a lazy learning algorithm and the outputs are found at time of execution.
Now the question is how do we determine the K value? Well, there is no proper statistical method to determine the optimal K value. Trial and error method is one of the ways to determine the K value but there is still a way to find an optimal K value. Define a range and plot a graph for error rate versus K values and the K value that gives the lowest error rate is the most optimal K value.
We will just quickly summarize it all for you and then we can move on the Notebooks section.
- Check the Type of problem statement you have. If it's a classification problem, KNN might be a good choice to go with.
- In KNN we calculate the Euclidean distance between the points in the plane and our target point.
- We define a K value and the K points having the least euclidean distance between them and our target points would determine our final output.
- There is no specific way to determine the K value but you can plot a graph of error rate versus K values and the one with least errror rate would be the optimal K value for our algorithm.
With KNN done, you can move onto the Notebooks and then implement whatever you have learnt so far in the Hands-on activity.
Implementation Walkthrough
Learn this section on Google Colab.