Support Vector Machine (SVM)
Support Vector Machine or SVM is one of the best algorithms when it comes to classification type problems and is very famous among ML Practitioners. In this section we will try and understand how it exactly works. Let's try and understand the whole working with a simple example. Let's say you are watching the republic day parade and there are people standing at both ends of the road. These people are guarded by Police on both the ends and in between, the army is marching. On the right side of the road we have all females and on the left side of the road we have all males.
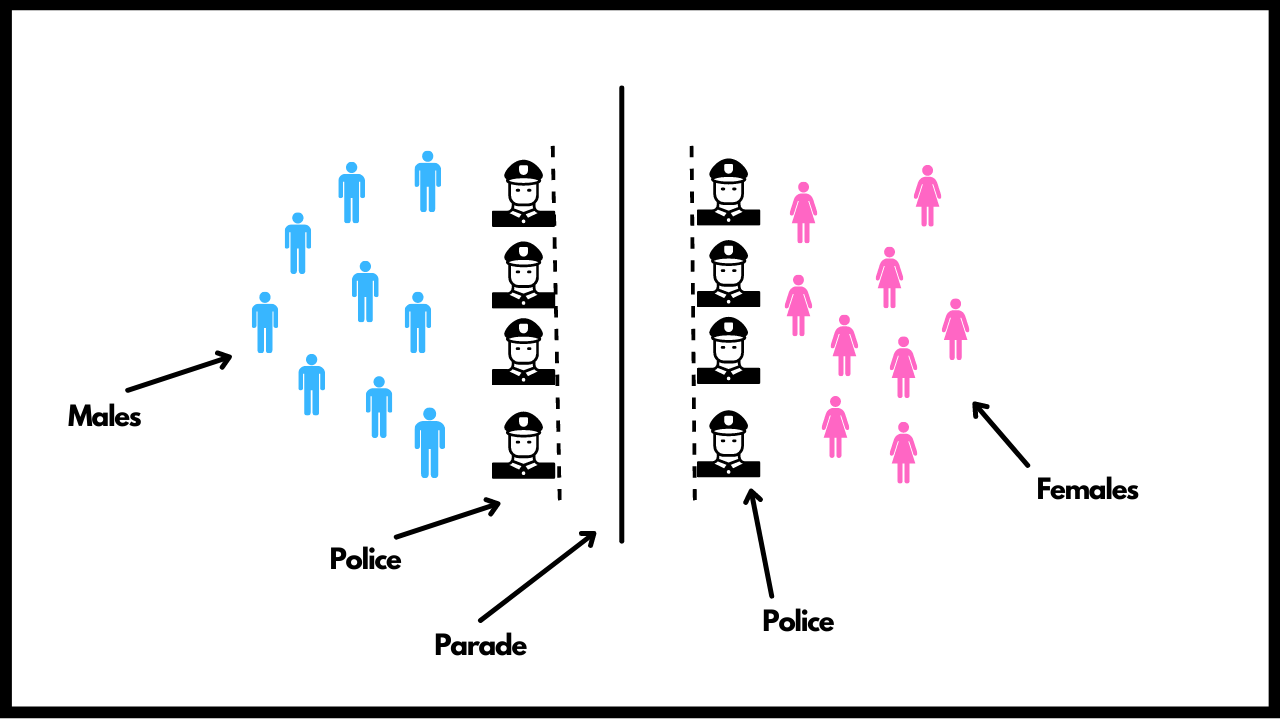
No person can cross the line created by the Police but each person is allowed to roam freely behind them. The above diagram is nothing but the whole setup of how the SVM works. Let us break it down for you. The people in the above diagram are the two classes or data points. Males are one class and females are the others. The road in between is the hyperplane dividing both these classes. The Police are nothing but the support vectors. So by this we can infer that, in SVM, we need to create a hyperplane that can easily classify the different classes present in our data. The support vectors help in determining the right hyperplane and hence this tells us that we only need a subset of all the data points to determine our hyperplane which would divide our classes in the best possible way and the behaviour of rest of the points won't affect it. These support vectors would remain closest to the border and the rest of points can be at any distance. Also, there must be some distance between our marching band and the police. This distance is known as the Margin.
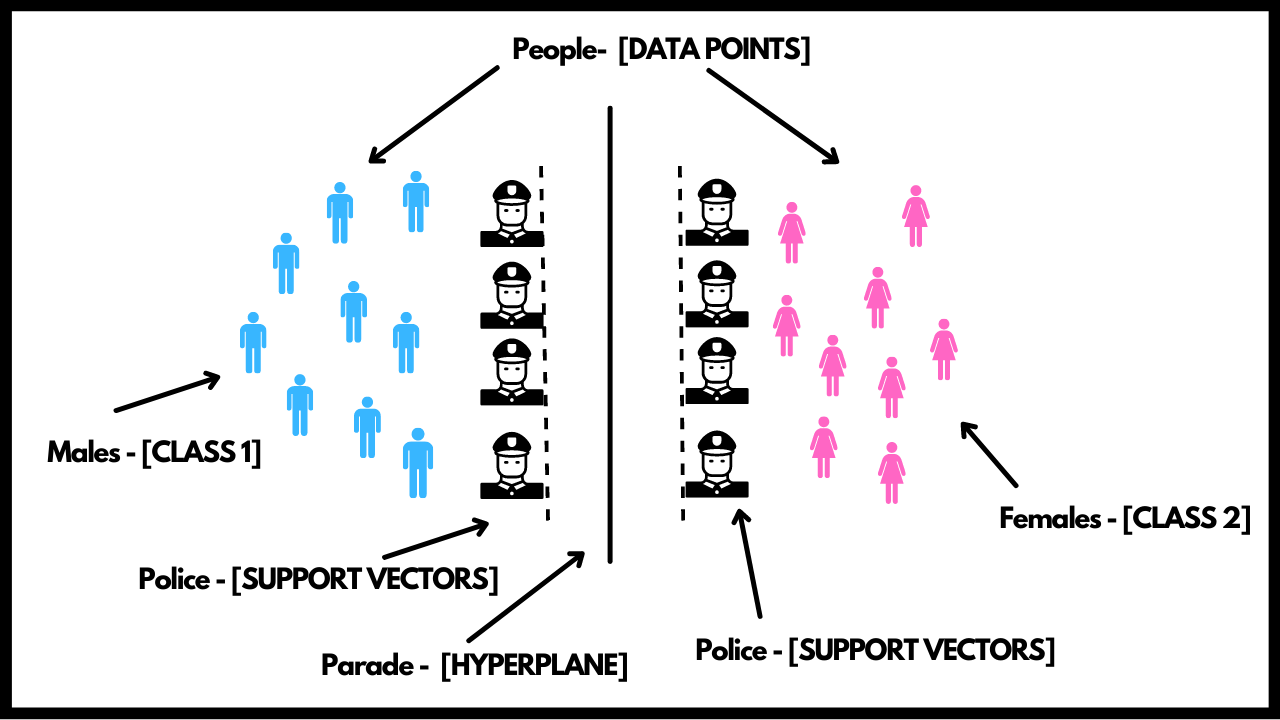
The goal is to maximixe the margin by making least error. In regards with the above example, the goal is to prevent maximum people from going close to the marching band and also increasing the distance between the band and the police. To understand this algorithm even better, we suggest you take a look at the Math section as well which will walk you through all the required maths. We also have the concept of linear and non-linear decision boundaries. In some cases you might enocunter a data which is not linearly seperable and in order to solve these problems, we make use of Kernel Trick. This helps in transforming the already existing fetaures in order to create new features in order to seperate them. This is a much more advanced topic and you can find more about it in the advanced section.
SVMs are preffered over some other classification models because they generate very accurate results even if the data is not linearly seperable. It is also very memory efficient. In practise, SVMs are more generalised which means they do not overfit. The only drawbacks that they have is that it takes lots of time to train the model inorder to find the right decision boundary and the final model that is created may not be interpretable.
With this we come to an end to our SVM theory. Let's quickly revise a few points:
- SVM are used mostly for classification type priblems.
- The idea is to create a hyperplane that divides two classes of the data and use only few points which we call support vectors in order to create this hyperplane.
- The goal is to minimize the number of points between the margin and the hyperplane and also to maximize the distance between the hyperplane and the margin.
- The other points apart from support vectors will not affect the hyperplane.
- SVM gives us very accurate results and hence one of the favourite algorithms for classification. It's also very memory efficient.
- Only drawback is that it takes longer amount of time to train as compared to other algorithms.
With this we come to an end to the SVM section and we can go on to the notebooks and Hands-on actiity to get some practical knowledge.
Implementation Walkthrough
Learn this section on Google Colab.